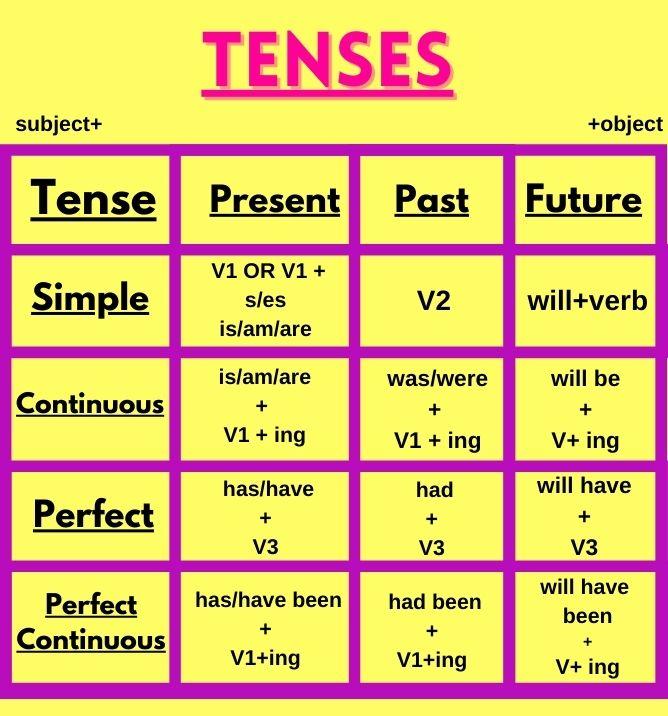
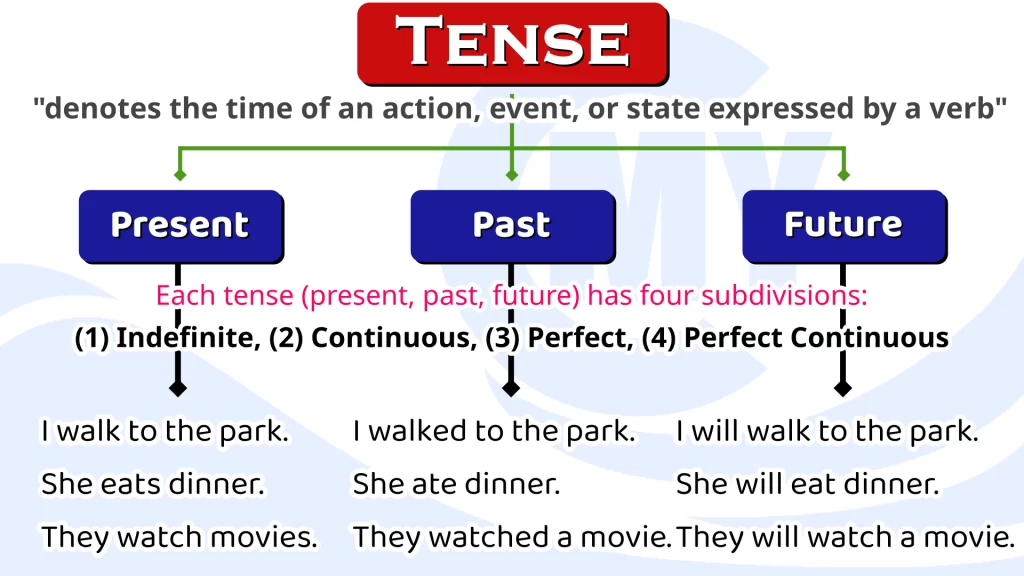
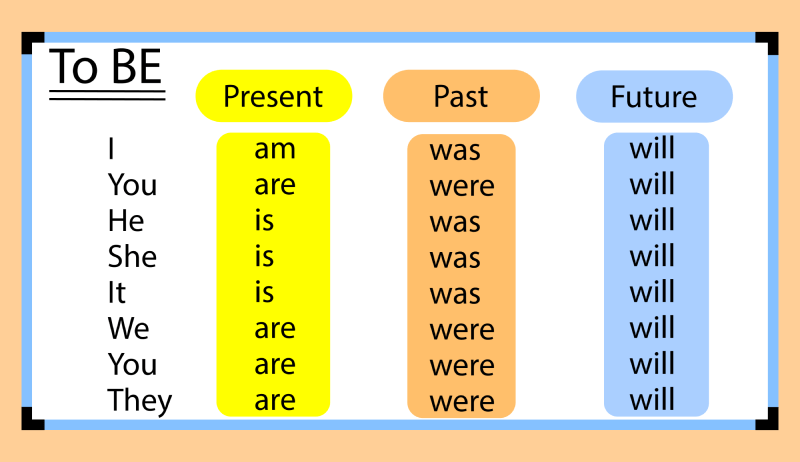
Certainly! The present tense in English grammar has four main forms:
Simple Present, Present Continuous (or Present Progressive), Present
Perfect, and Present Perfect Continuous. Let’s dive into each type in more
detail:
Simple Present
- Simple Present The simple present tense is used to express actions that
are habitual, general truths, or actions that happen regularly. It is formed by
using the base form of the verb (infinitive without “to”) for most subjects,
while the third person singular (he, she, it) adds an “s” to the verb.
- Habitual Actions: She reads books every night.
- General Truths: The Earth revolves around the Sun.
- Scheduled Events: The train leaves at 7 AM tomorrow.
- Instructions and Directions: Mix the ingredients and then bake the cake.
- Present Continuous (Present Progressive): The present continuous
tense is used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of
speaking, temporary actions, and future actions that have been planned.
- Current Actions: He is reading a book right now.
- Temporary Actions: She is staying with her friend for a few days.
- Future Plans: They are going to the beach this weekend.

Present Perfect
- Present Perfect: The present perfect tense is used to express actions
that have a connection to the present, even though they occurred in the
past. It often emphasizes the result of the action rather than the action
itself.
- Completed Actions with Relevance to Present: I have finished my
homework. - Unspecified Time in the Past: They have visited that museum before.
- Experiences in Life: She has traveled to many countries.
- Present Perfect Continuous: The present perfect continuous tense is
used to show actions that started in the past, have continued up to the
present, and might continue into the future. It emphasizes the duration or
ongoing nature of the action.
- Actions with Duration: They have been working on the project for hours.
- Emphasis on Continuous Activity: She has been studying for the exam.
- Recent Activities: He has been playing the guitar all afternoon.
Remember that the choice of present tense depends on the context and
the specific meaning you want to convey. Different present tenses help to
describe actions in various ways, whether they’re ongoing, habitual,
completed but relevant, or ongoing with a focus on duration.
4 types of past tense in details
Certainly! The past tense in English grammar has four main forms: Simple
Past, Past Continuous (or Past Progressive), Past Perfect, and Past Perfect
Continuous. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
Simple Past
- Simple Past: The simple past tense is used to describe actions that were
completed in the past. It doesn’t emphasize the duration of the action but
rather focuses on the fact that it happened. Regular verbs usually form the
past tense by adding “-ed” to the base form, while irregular verbs have
specific past tense forms.
- Completed Actions: She visited her grandparents last weekend.
- Past Events: They watched a movie yesterday.
- Specific Times in the Past: He studied for his exam last night.
- Sequential Actions: First, she woke up, then she ate breakfast.
Past Continuous
- Past Continuous (Past Progressive): The past continuous tense is used
to describe actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific point in
the past. It emphasizes the duration of the action and can be used to set
the scene or describe background actions.
- Ongoing Actions: They were playing soccer when it started raining.
- Interrupted Actions: She was reading a book when the phone rang.
- Describing Background: While he was cooking, they were setting the table.
Past Perfect
- Past Perfect: The past perfect tense is used to show that an action
happened before another action in the past. It emphasizes the sequence of
events and indicates that one action was completed before another took
place.
- Sequence of Past Actions: By the time I arrived, they had already eaten
dinner. - Background for Past Events: She had visited Paris before she met him.
- Actions Before a Certain Point: He had finished the report by the time the
meeting started.
Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Continuous: The past perfect continuous tense is used to
describe actions that were ongoing in the past, leading up to a specific
point or another action in the past. It emphasizes the duration and
continuity of the action.
- Duration Leading to Past Event: They had been studying for hours before
the exam. - Emphasizing Duration: By the time he left, I had been waiting for hours.
- Past Activities with Continuity: She had been working on the project since
morning.
Each past tense form serves a different purpose in describing actions or
events that took place in the past. Choosing the right past tense depends
on the context you’re trying to convey and how the timing of actions
relates to each other.
4 types of future tense in details
Certainly! The future tense in English grammar has four main forms: Simple
Future, Future Continuous (or Future Progressive), Future Perfect, and
Future Perfect Continuous. Let’s delve into each type in more detail:
Simple Future
- Simple Future: The simple future tense is used to express actions that
will happen in the future. It is often used for predictions, plans, intentions,
and spontaneous decisions.
- Predictions: It will rain tomorrow.
- Plans and Intentions: She will travel to Europe next year.
- Offers and Promises: I will help you with your project.
- Spontaneous Decisions: I’m hungry; I think I will have pizza for lunch.
- Future Continuous (Future Progressive): The future continuous tense
is used to describe actions that will be ongoing or in progress at a specific
point in the future. It emphasizes the duration of the action.
- Ongoing Actions: They will be celebrating their anniversary at this time
tomorrow. - Predictions with Certainty: He will be working on his assignment this time
next week. - Planned Actions: She will be traveling during the summer holidays.
- Future Perfect: The future perfect tense is used to show that an action
will be completed before another action or a specific point in the future. It
emphasizes the completion of an action.
- Action Before Another Future Event: By the time you arrive, I will have
finished cooking dinner. - Predictions and Expectations: They will have completed the project by the
deadline. - Hypothetical Situations: If they leave now, they will have reached the
destination by nightfall.
- Future Perfect Continuous: The future perfect continuous tense is used
to describe actions that will have been ongoing up to a specific point in the
future. It emphasizes the duration and continuity of the action leading up
to that point.
- Duration Leading to a Future Event: By this time next year, he will have
been working at the company for a decade. - Emphasizing Duration: They will have been traveling for two weeks by the
time they return. - Expectations and Speculations: I’m sure they will have been practicing
diligently for the competition.
Choosing the appropriate future tense depends on what you want to
convey regarding the timing, duration, and relationships between future
actions. Each form has its own nuance and is used to express different
aspects of events that will happen in the future.