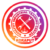
What is series circuit ?
In a series circuit, all components are connected end-to-end to form a single path for current flow. The total resistance in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual resistors, and the total voltage drop is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops across those resistors.
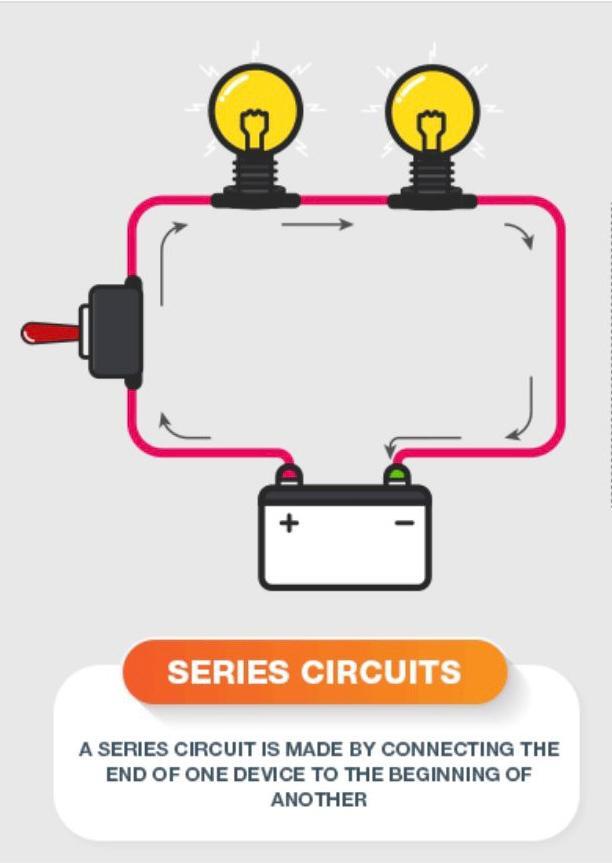
What is parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit comprises branches so that the current divides and only part of it flows through any branch. The voltage, or potential difference, across each branch of a parallel circuit is the same, but the currents may vary.
The major difference between series and the parallel circuit is the amount of current that flows through each of the components in the circuit. In a series circuit, the same amount of current flows through all the components placed in it. On the other hand, in parallel circuits, the components are placed in parallel with each other due to which the circuit splits the current flow. The current flowing from the source will be divided into the current flowing through each of these components.
Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuits
SERIES :-
- The same amount of current flows through all the components
- When resistors are put in a series circuit, the voltage across each resistor is different even though the current flow is the same through all of them.
- If one component breaks down, the whole circuit will burn out.
- In an electrical circuit, components are arranged in a line
- If V+ is the total voltage then it is equal to V1 + V2 +V3
PARALLEL :-
- The current flowing through each component combines to form the current flow through the source.
- In an electrical circuit, components are arranged parallel to each other
- When resistors are put in a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the resistors is the same. Even the polarities are the same
- Other components will function even if one component breaks down, each has its own independent circuit
- If Vt is the total voltage then it is equal to V1=V2=V3