History of Measuring Instruments Ancient Times Early humans used body parts like hands and feet to measure distances and objects.Middle Age More sophisticated measuring instruments began to emerge during the Middle Ages, such as the astrolabe and the quadrant.Industrial Revolution During the Industrial Revolution, the need for precision measurement led to the invention of new instruments like the micrometer and vernier caliper.Modern Times Today, measuring instruments continue to evolve with the advancement of technology, leading to more precise and efficient too.
Principles of Precision Measuring
AccuracyPrecision instruments must give accurate results.ReproducibilityInstruments must give the same measurements when used by different people.SensitivityThe instruments must be sensitive enough to measure the smallest possible change.ConsistencyResults of measurements should be consistent and repeatable.
Types of Measuring Instruments
Length:- Measuring tapes, calipers, and micrometers are used to measure length.
Angle:- Protractors, goniometers, and clinometers are used to measure angles.
Mass:-Balance scales, spring scales, and digital scales are used to measure mass.
Time:- Stopwatches, timers, and clocks are used to measure time.
Types of Measuring Instruments
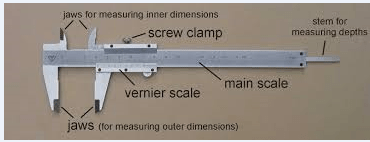
1.Vernier Caliper
Used for measuring the distance between two opposite sides of an object with high accuracy.
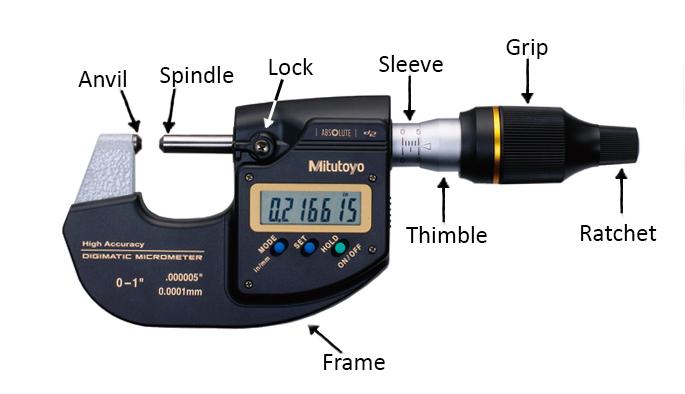
2.Digital Micrometer
Used to measure the thickness or diameter of small parts with sub-micron resolution.
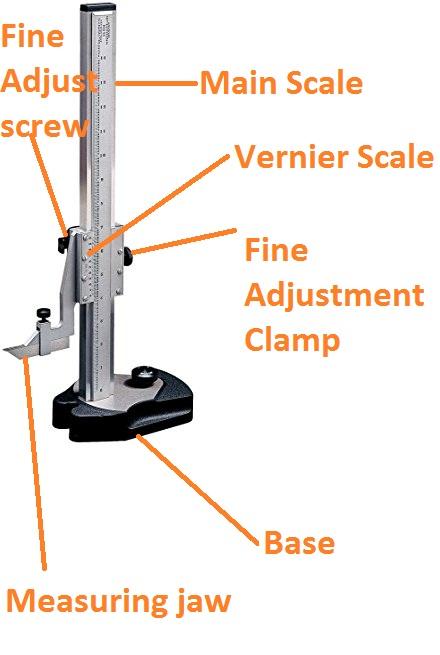
3.Height Gauge
Used to measure the height of objects with extreme precision for machining operations or inspection
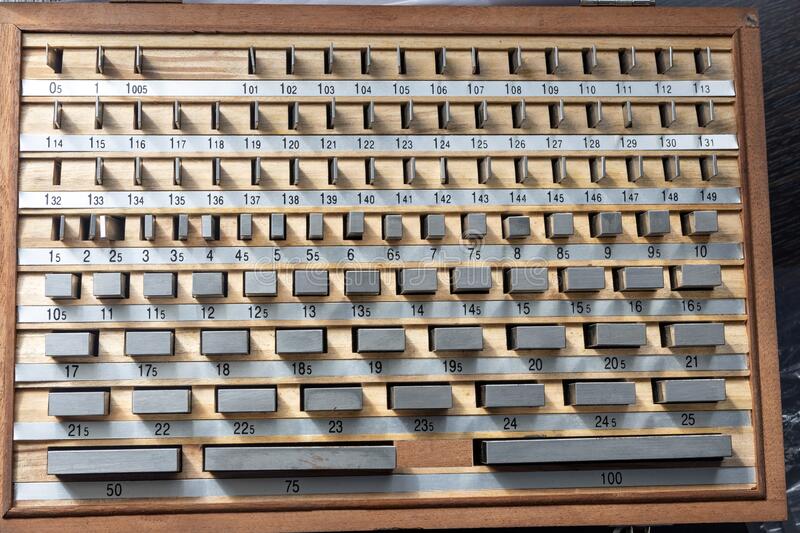
4.Gauge Blocks:-
A set of metal blocks used for precision measurement of length, thickness and step.

Maintenance
To maintain proper accuracy, measuring tools must be cleaned and periodically calibrated. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance.Maintenance and Calibration of Precision Measuring Instruments Regular Maintenance Keep your measuring instruments clean and safe from damage by regularly ensuring they are properly calibrated and well maintained.CalibrationCalibration is the process of ensuring an instrument’s accuracy in line with its initial settings, either by adjustment or by comparing it with those of a known accurate device.Regular Checkup Get your instruments checked on a regular basis to ensure continued accuracy. Preventative checkups can reduce repair costs and keep your instruments in good working condition