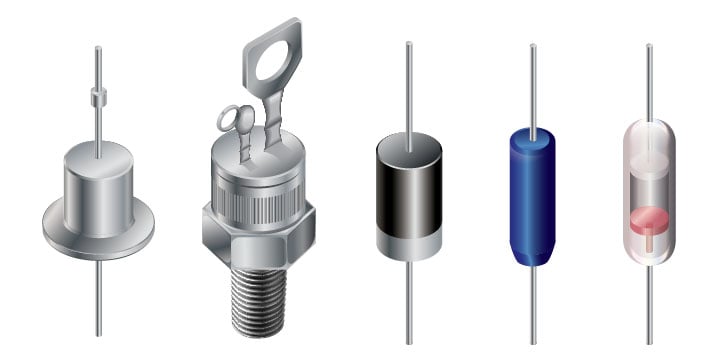
What is Diode
A diode is a semiconductor device that essentially acts as a one-way switch for current. It allows current to flow easily in one direction but severely restricts current from flowing in the opposite direction.
Diodes are also known as rectifiers because they change alternating current (ac) into pulsating direct current (dc). Diodes are rated according to their type, voltage, and current capacity.
Diodes have polarity, determined by an anode (positive lead) and cathode (negative lead). Most diodes allow current to flow only when a positive voltage is applied to the anode. A variety of diode configurations are displayed in this graphic:
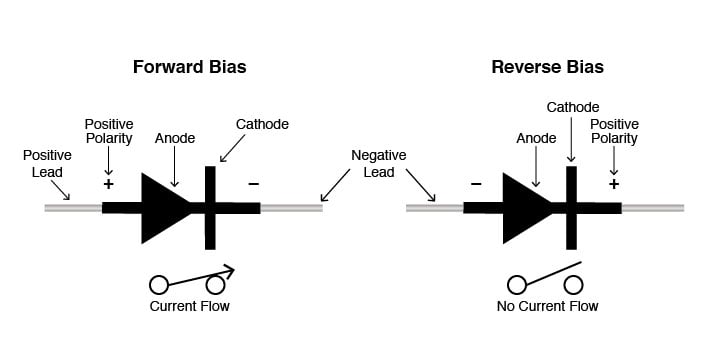
When a diode allows current flow, it is forward-biased. When a diode is reverse-biased, it acts as an insulator and does not permit current to flow.
Strange but true: The diode symbol’s arrow points against the direction of electron flow. Reason: Engineers conceived the symbol, and their schematics show current flowing from the positive (+) side of the voltage source to the negative (-). It’s the same convention used for semiconductor symbols that include arrows—the arrow points in the permitted direction of “conventional” flow, and against the permitted direction of electron flow.
A digital multimeter’s diode test diode produces a small voltage between the test leads enough to forward-bias a diode junction. Normal voltage drop is 0.5 V to 0.8 V. The forward-biased resistance of a good diode should range from 1000 ohms to 10 ohms. When reverse-biased, a digital multimeter’s display will read OL (which indicates very high resistance).

Diodes are assigned current ratings. If the rating is exceeded and the diode fails, it may short and either a) allow current to flow in both directions or b) halt current from flowing in either direction.

Reference: Digital Multimeter Principles by Glen A. Mazur, American Technical Publishers.
Types of Diodes
- Light Emitting Diode
- Laser diode
- Avalanche diode
- Zener diode
- Schottky diode
- Photodiode
- PN junction diode
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Laser Diode
It is a different type of diode as it produces coherent light. It is highly used in CD drives, DVDs and laser devices. These are costly when compared to LEDs and are cheaper when compared to other laser generators. Limited life is the only drawback of these diodes.
Avalanche Diode
This diode belongs to a reverse bias type and operates using the avalanche effect. When the voltage drop is constant and is independent of current, the breakdown of the avalanche takes place. They exhibit high levels of sensitivity and hence are used for photodetection.
When an electric current between the electrodes passes through this diode, light is produced. In other words, light is generated when a sufficient amount of forwarding current passes through it. In many diodes, this light generated is not visible as there are frequency levels that do not allow visibility. LEDs are available in different colours. There are tricolour LEDs that can emit three colours at a time. Light colour depends on the energy gap of the semiconductor used.
Zener Diode
It is the most useful type of diode as it can provide a stable reference voltage. These are operated in reverse bias and break down on the arrival of a certain voltage. If the current passing through the resistor is limited, a stable voltage is generated. Zener diodes are widely used in power supplies to provide a reference voltage.
Schottky Diode
It has a lower forward voltage than other silicon PN junction diodes. The drop will be seen where there is a low current and voltage ranges between 0.15 and 0.4 volts at that stage. These are constructed differently in order to obtain that performance. Schottky diodes are highly used in rectifier applications.
Photodiode
A photo-diode can identify even a small amount of current flow resulting from the light. These are very helpful in the detection of the light. This is a reverse bias diode and is used in solar cells and photometers. They are even used to generate electricity.
P-N Junction Diode
The P-N junction diode is also known as the rectifier diode. These diodes are used for the rectification process and are made up of semiconductor material. The P-N junction diode includes two layers of semiconductors. One layer of the semiconductor material is doped with P-type material and the other layer with N-type material. The combination of these both P and N-type layers forms a junction known as the P-N junction. Hence, the name P-N junction diode.