INTRODUCTION:-
The cold chisel is a hand cutting tool used by fitters for chipping and cutting off operations. Chipping is an operation of removing excess metal with the help of a chisel and hammer chipped surfaces being rough they should be finished by filling.
CHISEL IS TWO TYPES
- Hot chisel
- Cold chisel
PART OF A CHISEL
A part of chisel has the
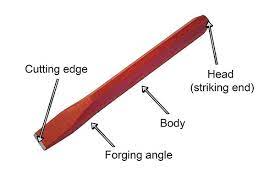
- Head
- Body
- Forging angle
- Cutting edge
How Many Types of Chisels?
There Are Five Common Types of Chisels
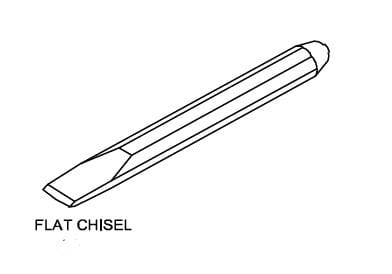
1.Flat Chisels:-
They are used to remove metal from large flat surfaces and chip excess metal off wield joints and casting.
2.CROSS CUT CHISELS:-
These are used for cutting keyways, grooves and slots.
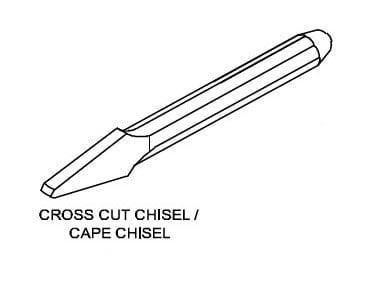
3.Half round nose chisels:-
They are used for cutting curved grooves coil grooves. These are used for squaring materials at the corners.

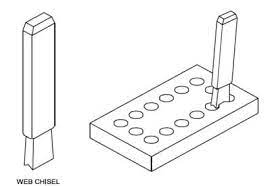
4.Web chisels:-
These chisels are used for separating metals after chain drilling.
5.Diamond point chisels:-
The meaning of diamond point chisels is a cold chisel having a diamond-shaped cutting face for cutting V grooves or sharp internal corners.

How to specified according chisels?
1.Length
2.Width of the cutting edge
3.Type
4.Cross-section of the body
The length of the chisels ranges from 150mm to 400mm .The width of the cutting edge varies according to the type of chisels.
Angles of chisels:
Point angles and materials:
The cutting angle of the chisel depends on the material to be chipped. Sharp angles are given for soft materials and wide angles for hard materials.
How much type of angle and what?
The angels chisel is two types
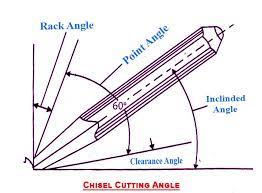
- Rake angle:-
Rake angle is the angle between the top face of the cutting point and normal to the work surface at the cutting edge.
2.Clearance angle:-Clearance angle is the angle between the bottom face of the point and tangent to the work surface at the cutting edge. The clearance angle is too low or zero the rake angle increases. The cutting edge cannot penetrate into the work. If the clearance angle is too great the rake angle reduces.
- SAFETY OF CHISEL
- Wear Safety Gear: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety goggles, gloves, and ear protection. This gear can shield you from flying debris, sharp chisel edges, and loud noise.
Maintain Sharp Blades: Contrary to what might seem intuitive, a sharp chisel is safer than a dull one. Sharp blades require less force, reducing the risk of slipping and injuring yourself.
Secure Your Workpiece: Ensure your workpiece is securely clamped or held in place. This prevents unexpected movements that can lead to accidents.
Use the Right Chisel for the Job: Different chisels are designed for specific tasks. Choose the appropriate chisel for your project to maximize safety and efficiency.
Keep Hands Away from the Cutting Edge: Always position your hands and fingers away from the path of the chisel blade. Consider using clamps or a vise to hold the workpiece.
Work with Controlled Force: Use controlled, even pressure when applying force to the chisel. Avoid excessive force that can lead to the chisel slipping and causing injuries.
Store Chisels Safely: When not in use, store chisels in a secure location, such as a toolbox or a chisel rack, to prevent accidental contact.
By following these chisel safety guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries while working with these versatile hand tools. Always prioritize safety to enjoy a productive and injury-free woodworking or crafting experienc
| SLNO | MATERIALS TO BE CUT | POINT ANGLR | ANGLE INCLINATION |
| 1 | High carbon steel | 65˚ | 39.5˚ |
| 2 | Cast iron | 60˚ | 37˚ |
| 3 | Mild steel | 55˚ | 34.5˚ |
| 4 | Brass | 50˚ | 32˚ |
| 5 | Copper | 45˚ | 29.5˚ |
| 6 | aluminum | 30˚ | 22˚ |