An electrical energy meter, also known as an electricity meter or simply a meter, is a device used to measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a residential, commercial, or industrial customer. It is an essential component of the electricity supply system and is typically installed at the point where electricity enters a building or facility.

The primary function of an electrical energy meter is to accurately measure the amount of electricity consumed over a specific period, usually in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It records the total energy consumption, enabling utility companies to bill customers accurately for the electricity they use.

Modern electrical energy meters are typically electronic devices that utilize various measurement techniques, such as current transformers and voltage sensors, to monitor the electrical current flowing through a circuit and the corresponding voltage. These measurements are then used to calculate the energy consumption based on the product of the current, voltage, and time.
In addition to measuring energy consumption, some advanced electrical energy meters also provide additional information, such as instantaneous power consumption, power factor, voltage fluctuations, and other parameters related to the quality and efficiency of the electrical supply.
Electrical energy meters play a crucial role in promoting energy efficiency, enabling utilities and consumers to monitor and manage their electricity usage. They facilitate accurate billing, support load balancing, and help identify patterns of energy consumption, which can be used to optimize energy usage and identify potential energy-saving opportunities.
An electrical energy meter, also known as an electricity meter or electric meter, is a device used to measure and record the amount of electrical energy consumed by a residential, commercial, or industrial facility. It is an essential component of the electricity billing system, allowing utility companies to accurately determine the amount of energy consumed by a customer and calculate the corresponding charges.
The electrical energy meter typically measures the amount of electrical energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is the standard unit of energy used by utility companies. It tracks the cumulative energy consumption over a specific period, usually monthly, and provides the readings necessary for billing purposes.
Modern electrical energy meters are generally digital and use electronic components to measure and record the energy consumption. They usually have a display that shows the current energy consumption, as well as additional information such as instantaneous power, voltage, and current. Some advanced meters may also offer features like remote reading, time-of-use tariffs, and communication capabilities for smart grid integration.
The accuracy of electrical energy meters is regulated by standards and regulations to ensure fair and reliable billing. Utility companies periodically test and calibrate meters to maintain their accuracy. Additionally, the advent of smart meters has enabled more precise measurements and improved energy management, allowing customers to monitor and optimize their energy usage in real-time.
An electrical energy meter, also known as an electricity meter or energy meter, is a device used to measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a residential, commercial, or industrial facility. It is commonly installed by utility companies to accurately determine the quantity of electricity consumed by a customer for billing purposes.
The energy meter typically measures the electrical power flowing through it and integrates this power over time to determine the total energy consumed. It records the amount of energy in units such as kilowatt-hours (kWh) or megawatt-hours (MWh).
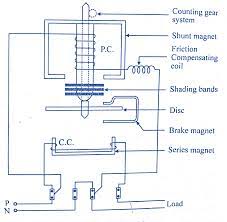
Electrical energy meters come in various types, including electromechanical meters and digital electronic meters. Electromechanical meters use mechanical components such as rotating disks and dials to measure energy, while digital electronic meters use electronic circuits and microprocessors for measurement and display.
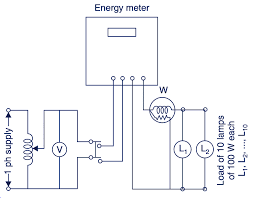
Energy meters are typically connected in series with the electrical supply line and measure the current and voltage of the electricity flowing into a facility. By multiplying the instantaneous current and voltage, the meter calculates the power consumption at any given moment. Integrating this power over time provides the total energy consumed.
These meters play a crucial role in determining accurate energy usage and facilitating fair billing for electricity. They are also essential for monitoring energy consumption, identifying inefficiencies, and promoting energy
There are several types of electrical energy meters used for measuring and monitoring electricity consumption. Here are some common types:
- Electromechanical Meters: These are traditional mechanical meters that use rotating disks to measure energy consumption. They typically have a series of dials or wheels that display the energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh).

- Electronic Meters: Electronic meters are digital devices that use solid-state technology to measure and display energy consumption. They often have a digital LCD or LED display and provide additional features such as time-of-use metering and data logging.

- Smart Meters: Smart meters are advanced electronic meters that enable two-way communication between the utility company and the consumer. They can remotely monitor energy usage, provide real-time data, and support features like demand response and dynamic pricing. Smart meters often have communication capabilities, such as cellular or RF communication, to transmit data.

- Prepaid Meters: Prepaid meters allow users to pay for electricity in advance. They typically have a built-in system that can be loaded with credits, which are then consumed as electricity is used. Prepaid meters help in managing energy consumption and avoiding unexpected bills.

- Multi-rate Meters: Multi-rate meters, also known as time-of-use (TOU) meters, measure electricity consumption at different rates based on the time of day. They are often used in tariff structures where electricity costs vary throughout the day, encouraging consumers to shift their usage to off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper.

- Three-Phase Meters: Three-phase meters are used in commercial and industrial settings where three-phase electrical systems are employed. These meters measure the energy consumption of each phase separately and provide a comprehensive view of the total energy usage.

- Clamp Meters: Clamp meters, also known as clamp-on meters or current clamps, are used to measure current flowing through a conductor without physically disconnecting the circuit. They can be useful for troubleshooting and measuring the energy consumption of individual appliances or devices.

It’s important to note that different regions and utility companies may have their own specific metering systems and terminology. The availability of these meter types may vary depending on the location and local regulations.
conservation in households and businesses.